Element 2.2 (Making the Management System Work
The Health and Safety Policy)
Making the Management System Work
The Health and Safety Policy
Introduction to Health and Safety Policies
An important document:
- The foundation stone for good health and safety management in an organisation.
- Sets out the organisation’s aims.
- Identifies who is responsible for achieving these aims.
- States how the aims are to be achieved.
- Specific to each organisation’s requirements.
(Not to be confused with ‘Policy’ in the H&S management system model.)
Group Discussion Point
- Why might the health and safety policy of two organisations be different?
- Why isn’t there a prescribed, ‘one size fits all’ approach to developing a policy?
- Why is an organisation’s health and safety policy so important?
- Why might two organisations doing similar work have different policies?
Standards and Guidance
Article 14
ILO Recommendation R164
Requires employers to set down in writing, policy and arrangements for health and safety management:
- Where circumstances warrant it.
- In a readily-understood language or medium.
The Three Parts of a H&S Policy
- Statement of Intent
▪️ What is going to be done. - Organisation
▪️ Who is going to do it. - Arrangements
▪️ How they’re going to do it.
General Statement of Intent
- Setting overall aims and objectives.
- Complying with law.
- Achieving standards.
- Reminds workers at all levels of their responsibilities.
- Signed and dated by the most senior person.
- Regular review.
Learning outcomes
At the end of this course, you will be able to:
- Explain the moral, legal and financial reasons for managing health and safety in the workplace
- Explain how health and safety is regulated and the consequences of non-compliance
- Summarise the main health and safety duties of different people at work
- Explain how contractors should be selected, monitored and managed
- Explain how accidents are caused and how to prevent them
- Recognise the key elements of a health and safety management system
- Explain why and how health and safety policies and procedures are implemented
- Explain how to check and improve health and safety performance
Setting SMART Objective
- Specific: clearly defined, precise.
- Measurable: Towards a target, quantified.
- Achievable: It can be done.
- Reasonable: Within timescale, and resources.
- Time-bound: Deadline, timescale.
Example: Review all 48 risk assessments within a 12-month period.
Setting SMART Objectives
NEBOSH-IGC
International General Certificate
It will be important to consider:
- Who is going to set the objectives.
- How objectives will be set at each functional level.
- Legal and other requirements.
- Hazards and risks.
- Technological options.
- Financial, operational and business requirements.
- Views of interested parties.
Group Exercise
- Targets may be included in the statement of intent to show commitment to improvement.
- What targets could be included? (General examples only needed.)
Organisational Roles and Responsibilities
- Outlines the chain of command for health and safety management.
- Identifies the roles and responsibilities of staff.
- Usually includes an organisational chart relating to health and safety.
- Shows lines of communication and feedback.
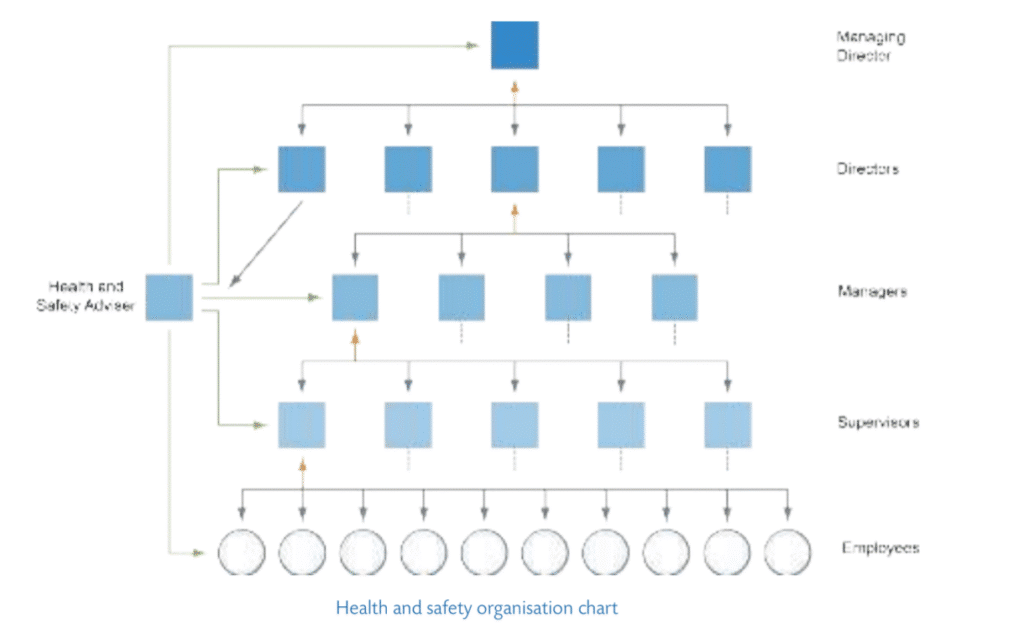
Organisational Roles and Responsibilities
Defines responsibilities for:
- The CEO or MD – ultimately responsible and accountable.
- Management – responsible for day-to-day management.
- All employees – responsible for acting safely.
- Competent persons – first aiders, fire marshals, etc.
- Specialist health and safety practitioners – responsible for providing advice to support management and employees.
Arrangements
- Describes how things are done.
- Detailed description of policies and procedures.
- Usually a long document.
- Often separate from the policy document.
- Unique to each organisation
Arrangements
General topics:
- Carrying out risk assessments.
- Information, instruction and training.
- Accident and near-miss reporting, recording and investigation.
- Consultation with workers.
- Developing safe systems of work.
- Welfare and first-aid provision.
- Fire safety and prevention.
- Emergency procedures.
- Compliance monitoring, including auditing
Individual Activity
Can you think of any other specific health and safety hazards?
Write down as many as you can think of, which you believe should be included in the Arrangements Section of a Health and Safety Policy.
Arrangements
Specific Risks and Problems
- Lone working.
- Noise-exposure control.
- Vibration-exposure control.
- Control of exposure to toxic materials.
- Control of crowds.
- Control of transport risks.
- Specific health surveillance requirements.
- Waste disposal.
Health and Safety Policies
- How can a policy be effectively communicated?
- When should it be reviewed?
Reviewing Policy
Changes in:
- Key personnel.
- Management structure.
- Processes.
- Technology.
- Legislation.
- Following an incident.
- As a result of enforcement action.
- After an audit.
- After worker consultation.
- Passage of time (Annually).